A Phase 1 Trial Demonstrates the Safety and Durability of SARS-CoV-2 DNA-Encoded Monoclonal Antibodies
Source: Nature Medicine (2025)
ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05293249
🧩 Overview
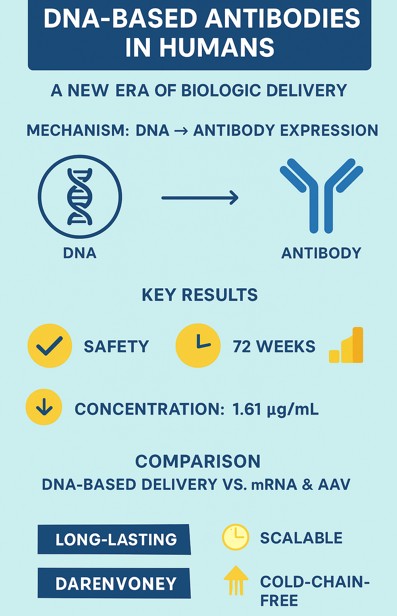
A groundbreaking phase 1 clinical trial has shown that synthetic DNA-based monoclonal antibody (DMAb) technology can safely generate durable antibody expression in humans — lasting over 72 weeks after administration. The study evaluated a plasmid DNA (pDNA) cocktail encoding AZD5396 and AZD8076, engineered versions of the tixagevimab/cilgavimab COVID-19 neutralizing antibodies.
Unlike traditional protein-based monoclonal antibodies, this platform delivers DNA constructs directly into muscle tissue, enabling the body to produce antibodies in vivo, offering a scalable, cold-chain-independent therapeutic strategy.
🧪 Key Findings from the Phase 1 Study
- Participants: 44 healthy adults enrolled; 39 completed full follow-up.
- Dosing: 1–4 intramuscular pDNA doses using the CELLECTRA® electroporation system.
- Safety: No product-related serious adverse events; well tolerated across cohorts.
- Expression: DMAbs detected in 100% of evaluable participants.
- Peak concentration: Up to 1.61 µg/ml; durable expression for 72 weeks.
- Functionality: Antibodies bound to multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants and showed neutralizing activity.
- Immunogenicity: No anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) detected across ~1,000 serum samples.
“This represents the first-in-human proof that synthetic pDNA can generate a functional monoclonal antibody cocktail in vivo,” the authors wrote.
⚙️ How DMAb Technology Works
DMAb (DNA-encoded monoclonal antibody) delivery involves:
- Plasmid DNA injection: Encoding antibody heavy and light chains.
- Electroporation (EP): Enhances DNA uptake into muscle cells.
- In vivo expression: Host cells synthesize fully functional antibodies.
- Sustained activity: Long-lived muscle fibers maintain expression without integration into the genome.
This approach eliminates the need for large-scale bioreactor production and cold-chain transport — key challenges for conventional biologics.
💡 Why It Matters
The success of this platform opens new possibilities for:
- Rapid antibody deployment during pandemics.
- Long-acting prophylaxis for infectious diseases.
- Accessible biologics for low-resource settings due to cold-chain independence.
- Scalable production, as plasmid DNA can be rapidly manufactured and stored at room temperature.
📈 Comparative Insights
- DMAb concentrations achieved (~1 μg/ml) are comparable to clinically active levels of several approved biologics, including:
- Columvi (Ctrough ≈ 590 ng/ml)
- Blincyto (Css ≈ 228–537 pg/ml)
- Kimmtrak (Css ≈ 13 ng/ml)
These findings highlight the therapeutic relevance of DNA-based antibody expression.
⚠️ Study Limitations
- Conducted in a single-center, homogeneous cohort.
- Larger, multi-ethnic studies are needed to assess scalability and variability.
- Expression levels, while biologically relevant, are lower than recombinant infusion peaks.
- Ongoing optimization may further enhance potency and duration.
🔭 The Future of DNA-Encoded Therapeutics
DNA-based delivery of monoclonal antibodies represents a transformative advance in biologics — merging gene therapy, immunology, and synthetic biology.
Future studies will explore broader applications, including:
- Chronic viral infections (e.g., HIV, Hepatitis B)
- Autoimmune diseases
- Oncology and metabolic disorders
This synthetic, nonviral, and scalable approach could revolutionize how antibodies and other biologics are delivered globally.
🔍 Meta Information
Meta Title:
DNA-Based Antibody Therapy Shows Long-Lasting Expression in Humans | Nature Medicine Phase 1 Trial
❓ FAQs
Q1: What is a DNA-encoded monoclonal antibody (DMAb)?
A DMAb is a synthetic DNA construct that encodes an antibody sequence, enabling the body to produce antibodies directly after injection — bypassing traditional manufacturing.
Q2: How is DMAb delivery different from mRNA vaccines or AAV vectors?
Unlike mRNA, DNA delivery offers greater stability and doesn’t require lipid nanoparticles. Unlike AAV, it avoids viral vector immunity and integration risks.
Q3: How long did antibody expression last in this study?
Antibodies remained detectable for up to 72 weeks, showing durable expression following intramuscular administration.
Q4: Were there any safety concerns?
No product-related serious adverse events or anti-drug antibodies were reported during the 72-week follow-up.
Q5: What are the potential applications of DMAb technology?
DMAbs could enable rapid, low-cost, and long-acting delivery of antibodies for infectious diseases, chronic conditions, and even cancer.
📘 Source: Nature Medicine (2025)
🔗 Clinical Trial: NCT05293249
Explore more
🎤 Career – Real career stories and job profiles of life science professionals. Discover current opportunities for students and researchers.
💼 Jobs – The latest job openings and internship alerts across academia and industry.
🛠️ Services – Regulatory support, patent filing assistance, and career consulting services.